성대의 자유연에 발생한 후두 지방종 1례
요약
Lipomas are benign tumors and most commonly occurs in trunk, upper extremities and lower extremities. About 13-15% of lipomas are located in the head and neck area. However, lipomas of larynx are very rare and only about 100 cases have been reported. Laryngeal lipomas occur mainly in epiglottis, aryepiglottic fold and false vocal cords, which have adipose tissue. Author experienced an unusual presentation of laryngeal lipoma. Tumor seemed to be located in the supraglottis in the preoperative laryngoscopy, but it was found to be located at the free margin of the true vocal cord. To date, only one case has been reported in the world literature. We report this case with a review of the literature.
Key words: Lipoma; Larynx; Vocal cords
중심 단어: 지방종; 후두; 성대
서 론
지방종은 양성 점막하 종양으로 체간이나 상하지에서 주로 발생하며 전체 지방종의 13~15%가 두경부에서 발생한다[ 1]. 하지만 후두에서 발생하는 지방종은 드물며 현재까지 약 100례가 보고되었다[ 2]. 후두에서 지방종이 발생하는 부위는 지방조직을 포함하고 있는 후두개, 후두피열주름, 가성대 부위이다. 후두 지방종은 위치나 크기에 따라 무증상부터 음성변화, 이물감, 연하장애, 호흡곤란을 보이는 경우도 있다[ 3- 5]. 저자들은 성대의 자유연에 발생한 매우 드문 양상의 지방종을 경험하였다. 국내에 보고된 적은 없었으며, pubmed 검색에서 단지 1례만이 비슷한 증례가 보고된 바가 있었다[ 6]. 이에 문헌고찰과 함께 증례 보고하는 바이다.
증 례
83세의 남자가 성대 종물을 주소로 이비인후과 외래에 내원하였다. 환자는 내원 1주전 외부병원에서 상부위장관 내시경을 시행하였고 성대용종 진단 하에 본원에 의뢰되었다. 환자는 2주 이상 전부터 애성이 있었으나 감기로 생각하고 특별한 검사는 시행하지 않았다. 과거력상 14년 전 위암으로 위절제술 시행 받았고, 고혈압 이외에 다른 병력은 없었다. 외래에서 시행한 후두경 소견상 황색의 비정형 종괴가 우측 성대 상부에서 관찰되었으며 후두실(ventricle)내로도 들어가 있는 양상을 보였다( Fig. 1A). 성대운동성은 정상이었다. 혈액검사상 혈색소 10.3 g/dL로 약간 낮았고, BUN, creatinine이 31.7 mg/dL, 1.43 mg/dL로 약간 상승한 소견 이외에 이상은 없었다. 전신마취 하에 후두미세수술을 시행하였다. 후두경을 이용하여 종양을 노출시키고 흡인기(suction)를 이용하여 종양을 당겼을 때, 외래에서 관찰한 경우와 달리 종양이 유경성(pedunculated)이었으며 성대상부가 아닌 진성대와 연결되어 있었다( Fig. 1B). 겸자(forceps)를 이용하여 당기면서 미세가위(microscissors)를 이용하여 제거하였다. 술 후 출혈이나 호흡곤란은 없었으며 수술 다음날 퇴원하였다. 육안소견상 0.8×0.6 cm 크기의 비정형의 연조직 종괴였으며 현미경소견상 주로 성숙한 지방세포로 구성되어 있으며 방추세포가 일부 포함되어 있었다. 면역조직화학검사상 지방세포에서 S-100이 양성, 지방세포와 방추세포에서 CD34가 양성을 보여 지방종에 합당한 소견이었다( Fig. 2). 수술 후 1주일째 추적관찰에서 성대는 잘 치유된 소견을 보였다( Fig. 1C).
고 찰
지방종은 체간이나 상하지에 주로 발생하는 양성종양으로, 전체 지방종의 약 13~15%가 두경부에서 발생한다[ 1]. 지방종은 다양하게 분류되는데, 최근의 분류에 의하면 위치에 따라 피하에 발생하는 피하 지방종(subcutaneous lipoma)과 근육내, 근육간, 관절, 신경 등 심부에 발생하는 심부 지방종(deep lipoma)으로 나누며 또한 동반하는 중간엽세포에 따라 혈관지방종(angiolipoma), 지방모세포종(lipoblastoma), 근지방종(myolipoma), 연골양지방종(chondroid lipoma), 골수지방종(myelolipoma), 방추세포/다형세포지방종(spindle cell/pleomorphic lipoma), 갈색지방종(hibernoma) 등으로 분류된다[ 7]. 지방종은 단발성 또는 다발성으로 발생하며, 다발성으로 발생하는 경우는 Launois-Bensaude’s syndrome(Madelung’s disease), adiposalgia, Adiposis dolorosa(Dercum’s disease) 등과 관련되어 있을 수 있다[ 8, 9]. 지방종의 병인으로는 배아 지방모세포나 이형성(metaplastic) 근육세포에서 발생한다는 설과 내분비계 이상, 외상, 감염, 만성자극 등이 원인이라는 가설이 있다[ 10]. 후두지방종은 육안적으로 황색의 평활하거나 분엽을 이루는 종괴로 보이며 점막하에 위치하거나 유경성으로 내강에 돌출하여 보일 수 있다. 병리조직학적으로는 편평상피 아래로 조밀한 섬유성 결체 조직들 및 확장된 림프관을 관찰할 수 있으며 그 아래로 성숙한 지방 조직 및 지방 조직 사이로 섬유 조직이 관찰되는 것이 특징적이다[ 11]. 후두지방종은 기도 폐색, 인두이물감, 음성변화, 코골이, 인후두부의 타액체류, 연하장애의 증상을 보일 수 있으며, 유경성 병변의 경우 발작적인 기침을 유발할 수 있다[ 3- 5]. Cantarella 등은 당시까지 후두 및 하인두 지방종은 약 80례가 보고되었으며, 후두에 발생하는 지방종은 주로 가성대, 후두개, 피열후두개 주름과 같이 지방조직을 포함하고 있는 부위에서 발생하며, 성대에 발생하는 지방종은 보고된 바가 전혀 없다고 하였다[ 12]. D’Antonio 등은 애성, 호흡곤란, 간헐적인 질식 발작을 보이는 63세 환자에서 진성대에 위치한 방추세포지방종을 처음으로 보고하였다[ 6]. 방추세포지방종은 점액양물질과 콜라겐섬유를 포함한 기질에 성숙한 지방세포와 방추세포(spindle cell)가 혼합되어 있는 지방종인데, 본 예의 경우에는 면역 조직검사상 CD34(+), S-100(-)인 방추세포 성분을 포함하고 있었으나, 일부에 국한되어 방추세포지방종보다는 단순 지방종으로 판단되었다. 지방종은 육안 및 내시경적 소견상 점액낭종(mucus retention cyst) 및 후두실(laryngocele)과 혼동될 수 있으며 영상학적 검사가 감별진단에 도움이 된다[ 1]. 영상학적 진단으로는 전산화단층촬영과 자기공명영상이 사용될 수 있으며, 지방조직의 영상학적 특징을 확인함으로써 가능하다. 전산화단층촬영에서는 -120~-60정도의 하운스필드단위(houndsfield units)로 물보다 낮은 감쇠치(attenuation value)를 보이며 조영 증강되지 않는다. 자기공명영상에서는 T1, T2 모두에서 피하지방과 같은 고신호강도(high signal intensity)를 보이며 지방억제(fat suppression)영상에서 명확히 억제되는 소견을 보인다[ 13]. 후두지방종의 치료는 본 예의 경우처럼 유경성이거나 크기가 작은 경우 내시경적으로 제거하며, 크기가 크고 심부에 위치하는 경우 경부절제가 필요하다. 드물긴 하지만 재발의 가능성이 있으므로 정기적인 추적관찰이 필요할 수 있다.
Figure 1.
Endoscopic findings. Yellowish mass was observed on the right vocal cord and extended into the right ventricle (A). During laryngeal microsurgery, mass was found to be connected to the free margin of the right vocal cord (B). On postoperative day 7, right vocal cord was healed well without residual mass (C). 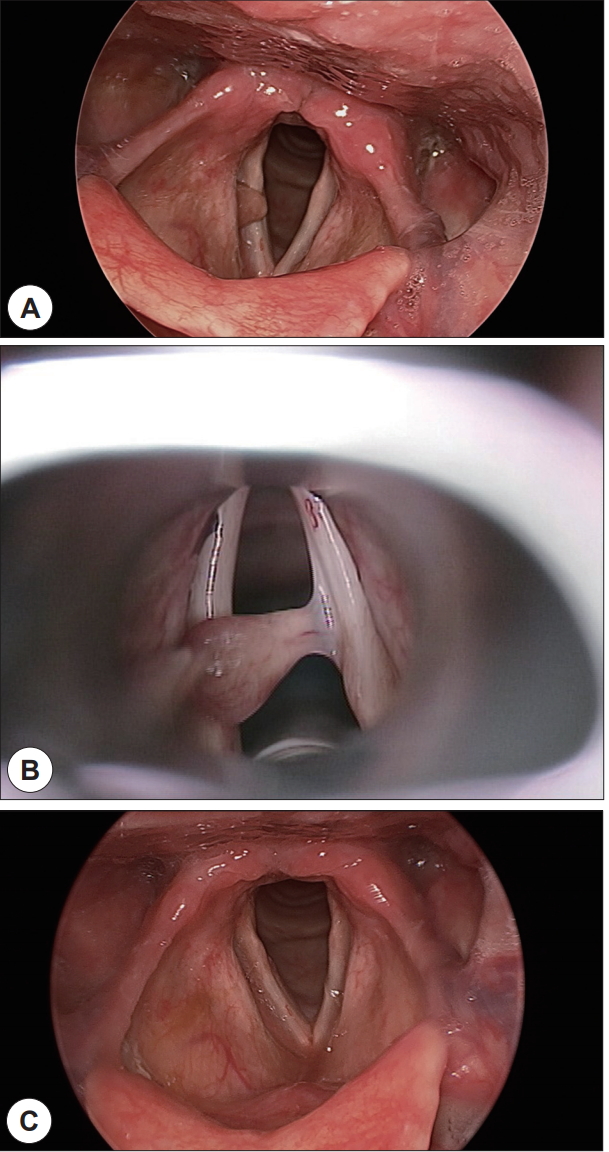
Figure 2.
Microscopic findings. Mass was covered by stratified squamous epithelium and consists of mature adipocytes with spindle cell components (H&E, ×40 and ×100) (A and B). In immunohistochemical staining, CD34 was positive in both adipocytes and spindle cells (×100) (C) but S-100 was positive only in adipocytes (×100) (D). 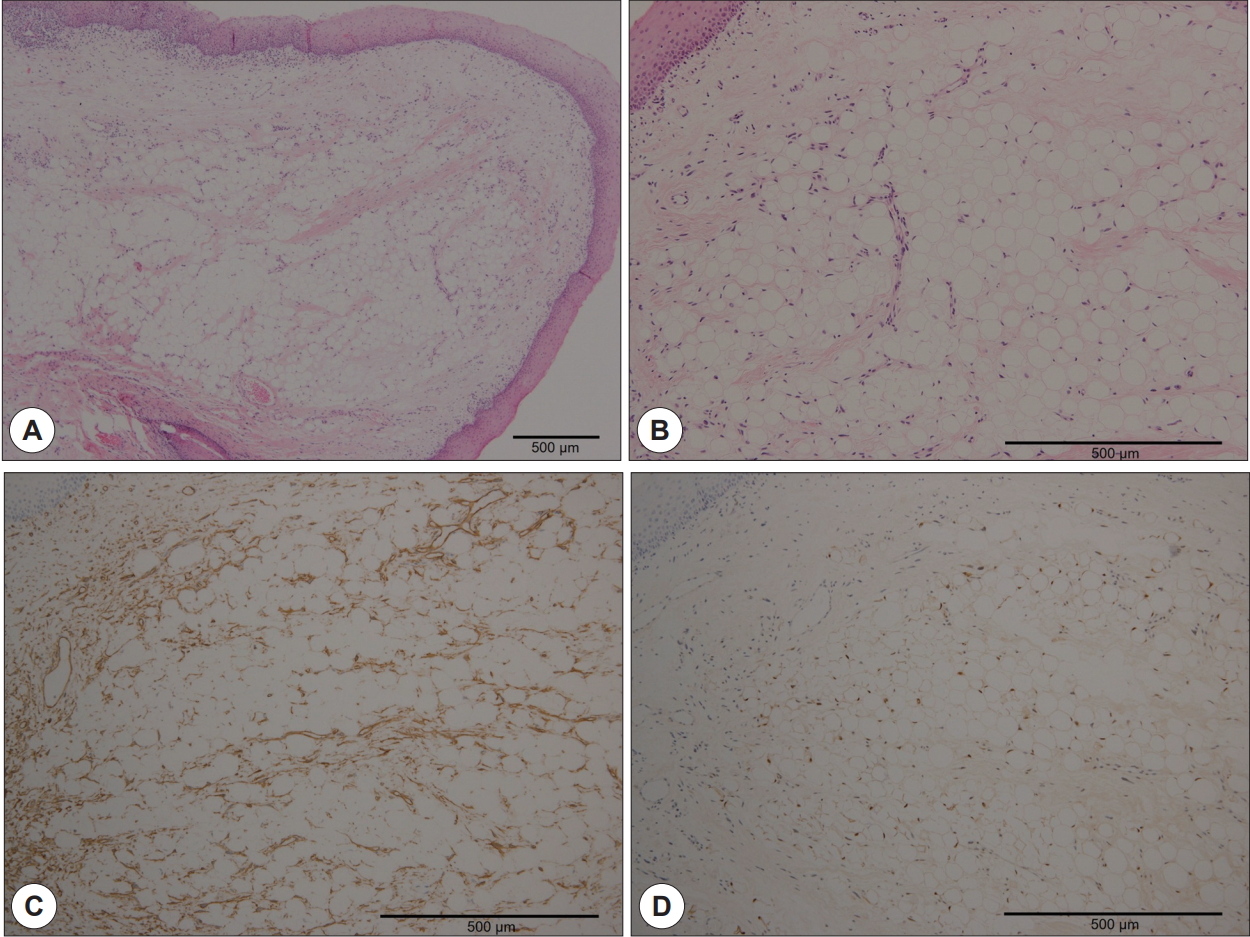
REFERENCES
1. Jungehülsing M, Fischbach R, Pototschnig C, Eckel HE, Damm M. Rare benign tumors: laryngeal and hypopharyngeal lipomata. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2000; 109( 3): 301- 5.   2. inghal SK, Virk RS, Mohan H, Palta S, Dass A. Myxolipoma of the epiglottis in an adult: a case report. Ear Nose Throat J 2005; 84( 11): 728 , 730, 734.   3. Khorsandi Ashtiani MT, Yazdani N, Saeedi M, Amali A. Large lipoma of the larynx: a case report. Acta Med Iran 2010; 48( 5): 353- 6.  4. Barry B, Charlier JB, Ameline E, Nallet E, Depondt J, Géhanno P. Retro-pharyngeal and pharyngeal-laryngeal lipomas. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 2000; 117( 5): 322- 6.  5. Moon TH, Lee DJ, Lee SJ, Jung PS. A Case of Lipoma of Epiglottis. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 2009; 52( 3): 270- 2.  6. D’Antonio A, Mottola G, Caleo A, Addesso M, Boscaino A. Spindle cell lipoma of the larynx. Ear Nose Throat J 2013; 92( 6): E9.  7. Mentzel T, Fletcher CD. Lipomatous tumours of soft tissues: an update. Virchows Arch 1995; 427( 4): 353- 63.   8. Kwon SH, Kim SC, Seo HS, Choi HS. Surgical Treatment of Two Cases of Benign Symmetrical Lipomatosis Causing Dyspnea. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 2006;49(7):758-62.
9. De Vincentiis M, Greco A, Mascelli A, Soldo P, Zambetti G. Lipoma of the larynx: a case report. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2010; 30( 1): 58- 63.   10. Wenig BM. Lipomas of the larynx and hypopharynx: a review of the literature with the addition of three new cases. J Laryngol Otol 1995; 109( 4): 353- 7.   11. Sarma NH, Ramesh K. Lipoma of the palatine tonsil. Histopathology 1996; 29( 1): 96- 7.  12. Cantarella G, Neglia CB, Civelli E, Roncoroni L, Radice F. Spindle cell lipoma of the hypopharynx. Dysphagia 2001; 16( 3): 224- 7.   13. Brisson M, Kashima T, Delaney D, Tirabosco R, Clarke A, Cro S, et al. MRI characteristics of lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma: retrospective comparison with histology and MDM2 gene amplification. Skeletal Radiol 2013; 42( 5): 635- 47.  
|
|













